All About Water - Water Quality, Water Filter, Water Resources and Issues
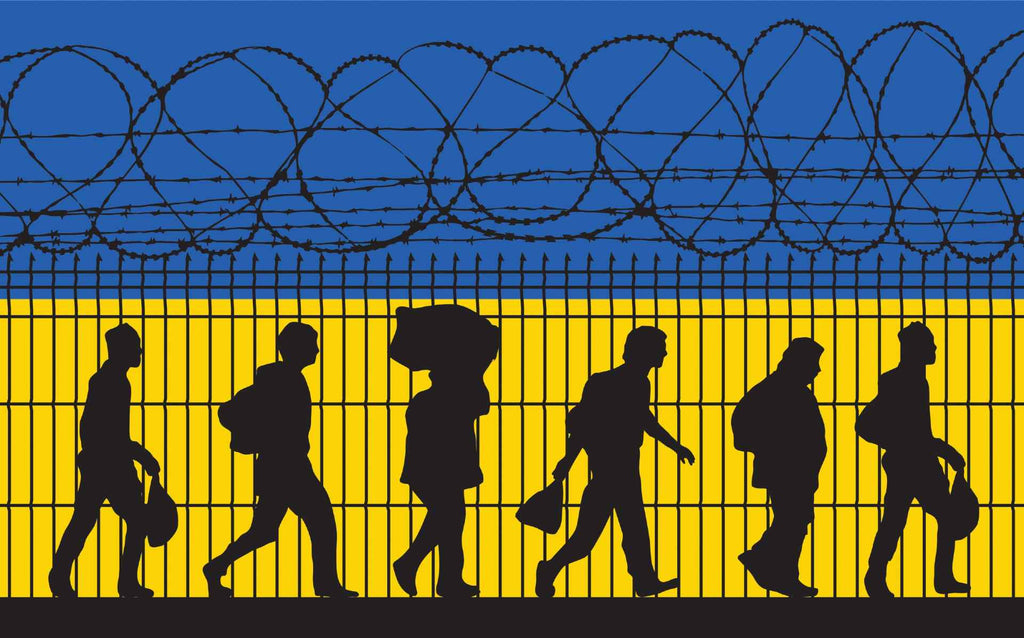
What should Americans know about the crisis in Ukraine?
Russia has assembled tens of thousands of troops along the Ukrainian border, an act of aggression that could lead to the biggest military conflict on European soil in many years. The armed conflict in Ukraine initially started in mid-2014. It immediately progressed to a long dead-end, with regular shelling and clashes happening along the forefront that isolated Russian and Ukrainian-controlled line borders in the east. Since Russia sent off a full-scale military attack on Ukraine on February 24, 2022, battling has caused more than 100 civilian casualties and pushed many Ukrainians to escape to neighboring...
Facts About Canada’s Water You Didn’t Know - Top 10 Highest Bottled Water Exporter
While 70% of the world is covered with water, freshwater accounts for just 1%. Of this 1%, only a tiny portion is available for consumption. Canada is renowned for its excellent ski resorts and the world's most famous waterfalls, so most expect it to be bountiful with fresh water. In any case, as the population grows, contamination levels rise, and urbanization expands, water consumption must be considered; this limited resource is under pressure every day. Matching these factors with natural changes to Canada's climate and water shortage could be a test that a few communities face later. Regardless, Canadians drink large amounts of...
Playing Too Much Video Games? Drink More Water!
While gaming used to be something, for the most part, enjoyed by younger individuals, this dynamic has changed over time. Limitless information has permitted games to be played on a mobile phone without agonizing over excess charges on your data allowance, cross-platform play allows gamers to partake in similar games on a wide range of gadgets, and the sheer assortment of games being delivered implies that there is practically something for everybody, paying little heed to age or sexual orientation. Last year, it was accounted for that there are presently over 3.24 billion gamers worldwide, and that...
Essentials List for Minimalist Living
Minimalism has hit the mainstream and is becoming more popular than ever. Even though it has been around for a long time, it should be an international trend! Many people have now applied a minimalist lifestyle in their homes. Some may think that minimalist homes lack character, fun, and life. But, many have proven that there is a sense of satisfaction and fulfillment in looking around and seeing a home free from clutter. It makes them calm and free and feels just lovely. Advantages of a Minimalist Home There are several benefits of keeping a minimalist lifestyle, but below is a...
What if the Oceans Disappeared? What if it Did Not Exist?
Oceans cover 71% of our planet. According to the U.S. Geographical Survey, there are approximately 321,003,271 cubic miles of water worldwide. That would be sufficient to fill about 352,670,000,000,000,000,000 gallon-sized containers. The ocean is vast and deep. This makes concentrating on it highly challenging. Researchers have precisely mapped just 5% of the ocean floor. The surface of the moon and Mars are more identified than we do about our sea depths. New technological innovations might ideally change this throughout the next few decades. However, what would happen to the planet without oceans, rivers, or lakes? It would look...
Future Farming: What Does Future Farming Look Like?
Farming is the foundation of every country and the source of all our food. So, it’s safe to say that every nation's population depends on it, maybe the smallest or the largest. Agriculture is the single largest employer in the world. It employs more than 24 million American workers (17% of the total workforce) and 40% of the global population. Food is one of the top critical survival factors, further explaining the significance of farming. Some interesting facts are provided below. (The data below are from the United States alone.) There are 914 million acres of farmland...
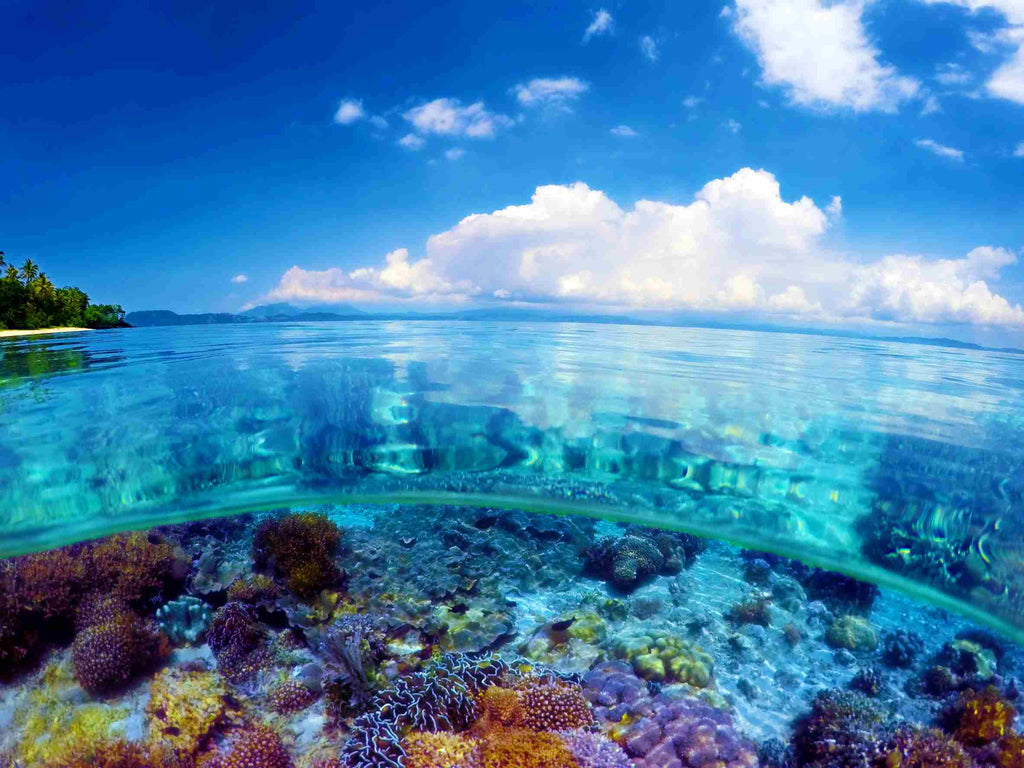
How Can We Save Coral? Coral Reefs Are In Danger
When you visualize a coral reef, images of brilliant corals, flawless blue water, and dynamic marine creatures ring a bell. Healthy coral reefs are colorful and extraordinarily biodiverse ecosystems. Indeed, while coral reefs make up about under 1% of the seafloor, they house almost 25% of life in the ocean. No wonder they are also called "the rainforests of the ocean.” However, aside from that, they are significant, both environmentally and economically. Why are Coral Reefs Important? Stating that coral reefs significantly benefit the marine ecosystem is just the icing. Coral reefs are...
Coronavirus(Covid-19) Dehydration Concerns - Stay Hydrated!
From how frequently you shower to how regularly you do your groceries, the COVID-19 pandemic has changed our everyday schedules, including how we approach drinking water. With plans changing so regularly, it's not difficult to neglect routines like keeping a water bottle in your work area that used to be essential for your everyday life. Our bodies are around 60% water, so it's essential to ensure we're focusing on our water intake, regardless of what's happening around us. Hydration is a vital foundation for ideal well-being and nourishment. Getting the perfect amount of liquids is critical for controlling internal...
The Color of Sky: Why Does it Look Blue or Red?
Today, the fast-paced life, financial crisis, and even social media are causing many individuals to feel exceptionally stressed. Numerous studies have proven that taking time to unplug, be with nature, and experience the outdoors positively affects one's physical and mental health. Moreover, openly staring at the sky can bring remarkable calm and healing! Research suggests that the curbed green light improves dopamine production in the brain and gives a calming feeling. Likewise, the blue sky causes a gentle sensory deprivation that will assist them with turning their attention inward and divert them from everyday stress. Yet,...
How to Feel Optimistic In Difficult Times
When you feel overwhelmed and discouraged about a significant life change, the last thing you need to hear are clichés about positivity. Having loved ones urge you to care for your problems might appear impossible and surprisingly offending. Just because you feel pessimistic about the possibilities for your life after divorce, custody changes, or other considerable changes in the world doesn't make you a pessimist. It is normal to battle self-worth issues and negative considerations. Indeed, even individuals who might portray themselves as positive thinkers battle these negative sentiments during difficult times. It's normal for these individuals who are...
Dangerous Brain-Eating Amoeba Spreading in the US
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have alerted that a dangerous brain-eating amoeba is gradually spreading across the United States. The single-cell amoeba Naegleria fowleri is typically found in warm freshwaters, such as lakes, rivers, ponds, and springs. It is also found in humid states like Florida. Often, the amoeba enters the body through the nose, where it heads to the brain. When the organism enters the brain through the olfactory nerves, it damages brain tissue and causes a harmful brain infection called primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). Although the infection is very uncommon, it is indeed fatal. The...
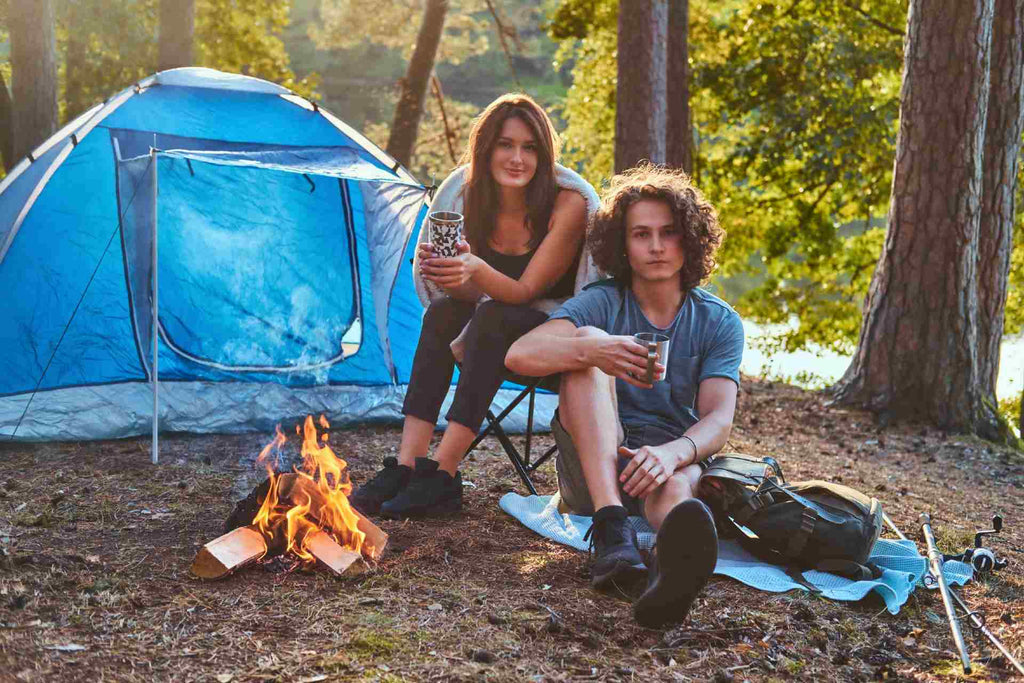
Best Tips on How to Stay Cool On Summer Camping
Summer is probably the best season for outdoor adventure. School is out for the year, the weather is fine, and you can generally figure out how to get away from work. It's the ideal time to pile stuff in your car, hit the road, and get lost in nature. Camping in summer is a perfect activity but can also be a double-edged sword. On the one hand, it is the season to get outside and unwind, enjoying the long, hot days and warm, beautiful evenings. On the other hand, waking up in a hot tent on a scorching...
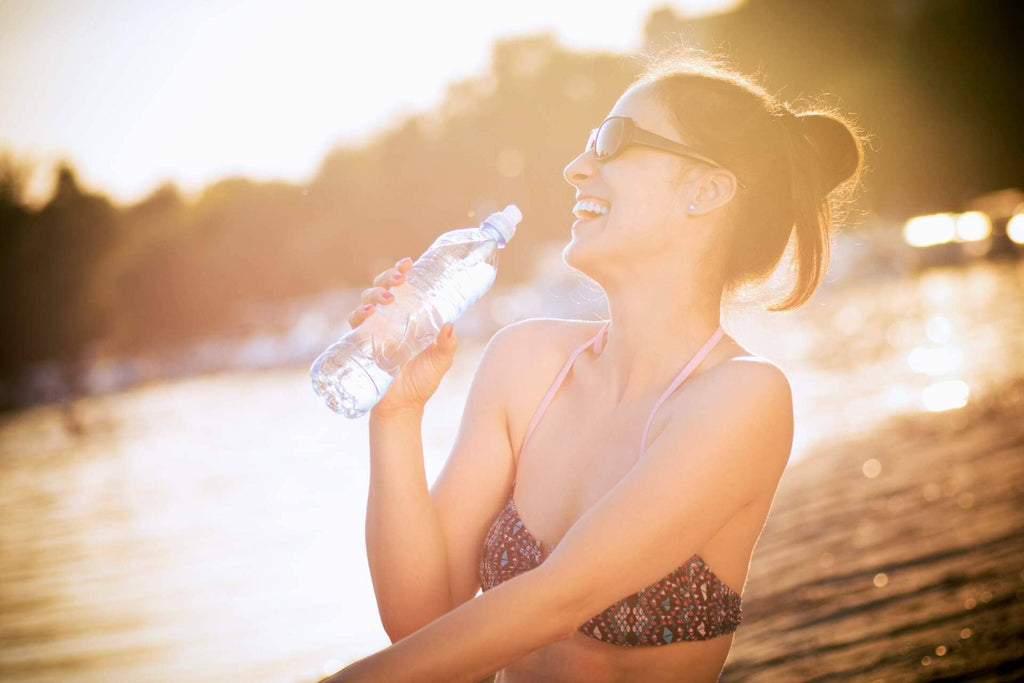
How to Stay Hydrated During the Summer Heat
Like it or not, the heat of the sunlight will always strike on us no matter what. All the more during the summer season! The long, sunny days and windy evenings of summer lure us to the outdoor activities. Trekking, swimming, and water activities are indeed the things you will explore so severely. Strolling along the seashores while enjoying the surf or exploring hiking trails has become the favorite pastime for many. However, summer likewise brings heat waves, and the rush of outrageous weather, especially in the first part of summer, is a...
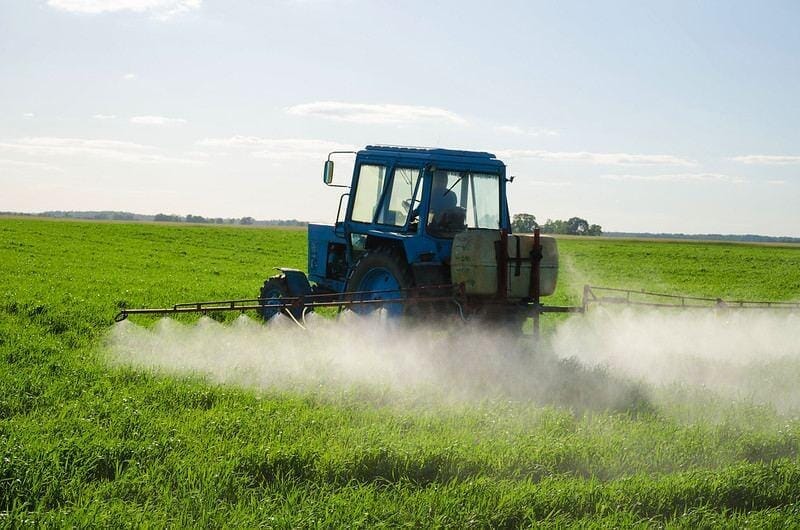
How to Remove Glyphosate from Drinking Water
Nothing beats a glass of ice-cold water quenching your thirst, especially in the summer heat. But often, you settle for knowing that it freshens up, and you think it is clean enough. NSF International, an independent product testing and certification association, reports that more than half of Americans worry about the water quality in their homes. As a result of reports in the news, numerous individuals know lead poisoning can significantly lessen the quality of municipal drinking water. Hard water, however non-toxic, can leave a residue on our skin and hair and an aftertaste...
How to Remove Haloacetic Acids in Drinking Water
Water is surely one of the most fundamental resources people need to survive. You need access to a dependable supply of safe drinking water to stay healthy and keep your body in good condition. One approach to guarantee that you generally have clean water inside reach is through water purification. According to the Koshland Science Museum, every individual on Earth needs 20 to 50 liters of safe water daily for drinking, cooking, and essential hygiene. Having a clear glass of water to quench your thirst seems safe enough. Little did you know that it probably contains...
Best Water for Brewing Tea and Coffee You Should Try
For all die-hards, the quality of your tea or coffee brand, or whether it is from high-quality coffee beans and tea leaves, does not matter. The consistency of the liquid, blending in the flavor, taste, and aroma, is important, as is the kind of water used when brewing. You must focus on water purity, hardness, temperature, and more. Thus, water is the main ingredient. These days, many people are experts in tea and coffee and frequently make their own versions of brews at home. You need that ideal first tea or coffee...
Danger of Lead Poisoning from Galvanized Steel Pipes
Homes constructed many years ago were kept to different regulations compared to residences and buildings built today. Houses built during the 1960s and prior were regularly outfitted with galvanized sewer/water pipe systems. These steel pipes were coated in a layer of zinc to broaden their powerful life span. While this seemed like a smart idea at the time, developers and health experts today realize that galvanized piping can cause various issues for both homes and homeowners. However, this old-fashioned and hazardous pipe material has been found in homes built before the 1980s. Galvanized piping comprises steel with an...
The Dangers of Drinking and Swimming Cold Water
Proper hydration is essential for working efficiently and for your complete health. Water is the best fluid for the body to drink, as it makes up around 65% of the body. It performs many essential functions, including waste disposal, regulating body temperature, and lubricating joints. It also transports hormones and nutrients to organs via the blood and helps in recovery from injuries. If you don't drink enough water, you may become dehydrated. Your body needs more liquid to function properly. Your urine can be a warning sign that you may be dehydrated. If it is colorless or...
What is Hydrogen Water? Does hydrogen water benefit our health?
Water is the healthiest beverage. Health experts have likely told you that staying hydrated is vital to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. You've presumably also heard from fitness instructors that drinking lots of water is one way to successfully get in shape. Time flies, and so do the innovations in this industrialized world. People didn’t only settle for drinking plain water. Many claim that adding elements to water will amplify the existing benefits and have a greater impact on wellness. Some commercial beverage companies consider hydrogen water useful for enhancing health benefits. Is this factual or a myth? Many are into this...
Water Quality at America's Beaches - Pollution, Contamination, and Unsafe Swimming Conditions
There is something in the sea breeze that gives you a sense of inner relaxation. All the more, swimming up to the best of your breath, exploring the depths of the sea. People even spend a long weekend at the beach by choice, savoring the fine sands under their toes, the beaming sunlight on their skin, and the calming crashing of the waves. The beaches in the United States showcase the natural, blissful scenery. That is worth spending your getaway with. Yet it is necessary to remember to sanitize the water you are to plunge into. It does not...